40 compare the movement of surface and deep currents
6A: Down to the Deep - The Ocean's Biological Pump Downwelling occurs when surface waters converge (come together), pushing the surface water downwards; regions of low primary productivity because nutrients get used up and are not continuously resupplied by the cold, nutrient-rich water from below the surface. currents occur in areas where cold, denser water sinks. These downwelling currents bring dissolved CO 2 down to the deep ocean. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Patch_clampPatch clamp - Wikipedia This leakage can be partially corrected for, however, which offers the opportunity to compare and contrast recordings made from different areas on the cell of interest. Given this, it has been estimated that the loose patch technique can resolve currents smaller than 1 mA/cm 2. Patch-Seq
What causes ocean currents?: Ocean Exploration Facts: NOAA ... There are two distinct current systems in the ocean—surface circulation, which stirs a relatively thin upper layer of the sea, and deep circulation, which sweeps along the deep-sea floor. Download image (jpg, 38.6 KB). Surface currents in the ocean are driven by global wind systems that are fueled by energy from the sun.

Compare the movement of surface and deep currents
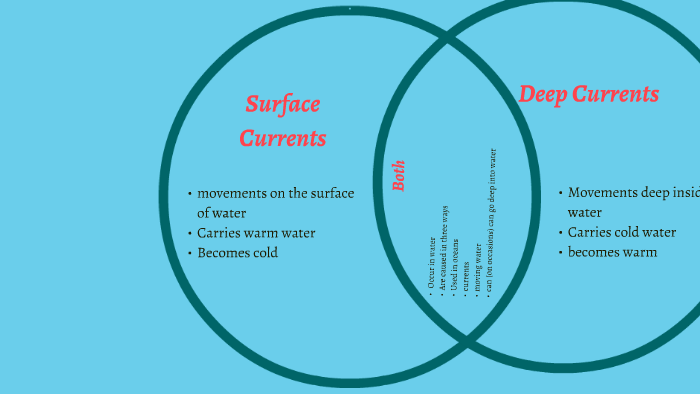
Earth's Waters 4-4 Notes Flashcards - Quizlet Compare and contrast surface currents and deep currents. They are both are moving water that flows through oceans. Surface currents are towards the top of the ocean, can be warm or cold, and are controlled by winds. Deep currents are low, deep in the ocean, cold, and are controlled by density. How does upwelling effect marine life? Surface currents vs. Deep currents by Cedric Wright Surface currents vs. Deep currents Occur in water Are caused in three ways Used in oceans currents moving water can (on occasions) can go deep into water Deep Currents Surface Currents Both Movements deep inside water Carries cold water becomes warm movements on the surface of PDF Ocean Currents and Sea Surface Temperature Part I: Obtain maps of sea surface temperature (SST) and ocean surface winds from the Live Access Server. 1. Click on the link for the Live Access Server. 2. Click on 'Choose Dataset' if it does not automatically appear. Select Oceans, Daily Sea Surface Temperature (GHRSST). 3. For region, have students select their own from the drop-down menu.
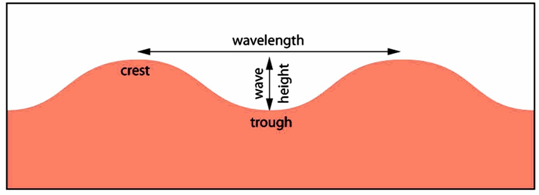
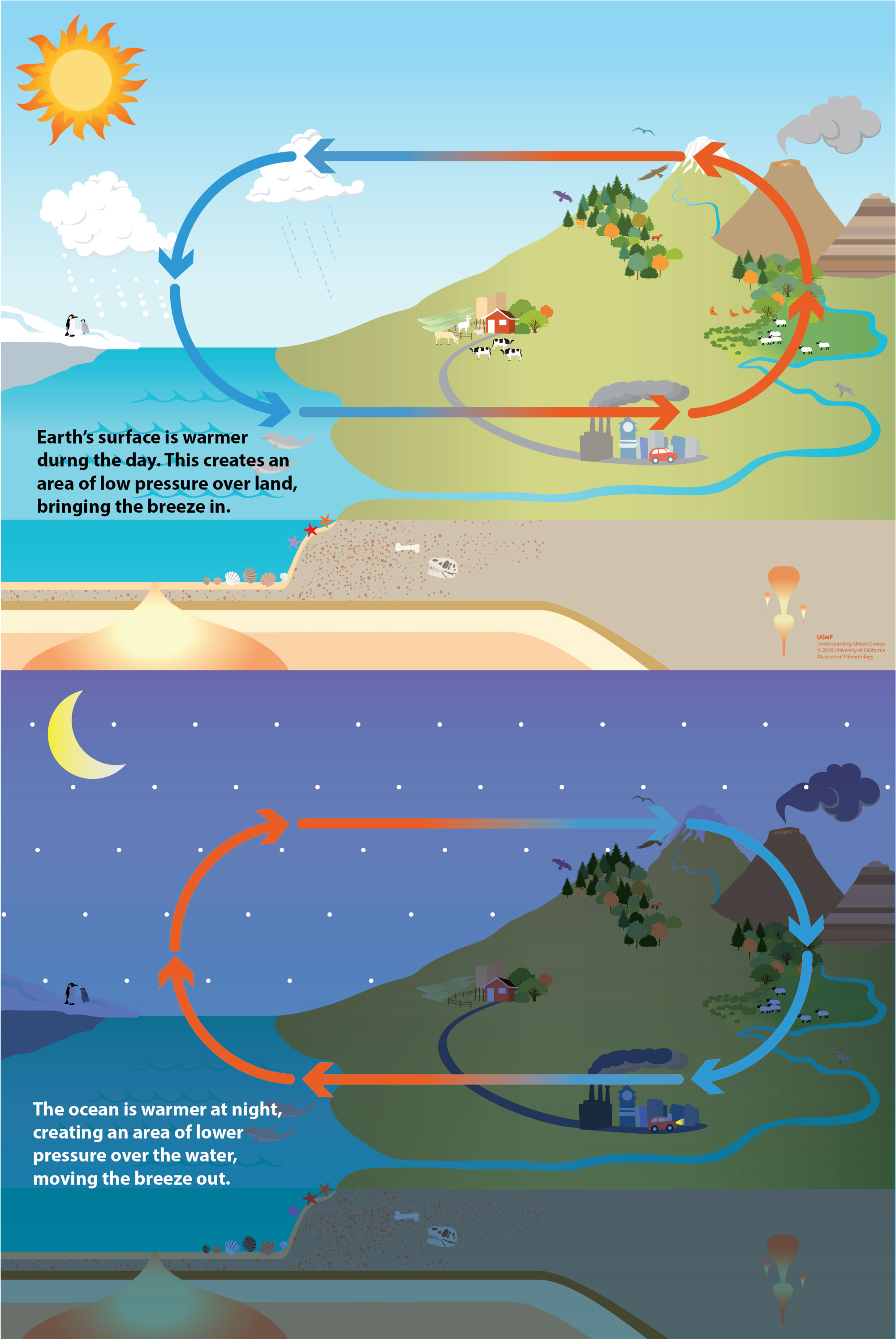
Compare the movement of surface and deep currents. d6cwmg2kst3of.cloudfront.net › documents › guide4th grade Energy & Waves disturbing the surface. When waves move across the surface of deep water, the water goes up and down in place; it does not move in the direction of the wave except when the water meets the beach. • Waves of the same type can differ in amplitude (height of the wave) and wavelength (spacing between wave peaks). 6* ,8 Satellite Applications for Geoscience Education Deep ocean currents (also known as Thermohaline Circulation) are caused by: The density of sea water varies globally due to differences in temperature and salinity. Surface water is heated by the sun, and warm water is less dense than cold water. Similarly, fresh water is less dense than salty water. manoa.hawaii.edu › exploringourfluidearth › nodeCompare-Contrast-Connect: Seismic Waves and Determining Earth ... SF Table 7.1 shows that P waves have a higher velocity than S waves when traveling through several mineral types. The speed at which seismic waves travel depends on the properties of the material that they are passing through. Modeling Salinity and Deep Ocean Currents - NASA The surface ocean current brings new water to this region from the South Atlantic via the Gulf Stream and the water returns to the South Atlantic via the North Atlantic Deep Water current. The continual influx of warm water into the North Atlantic polar ocean keeps the regions around Iceland and southern Greenland mostly free of sea ice year-round.
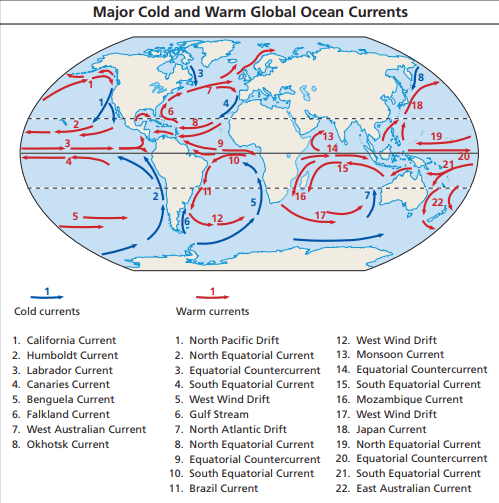
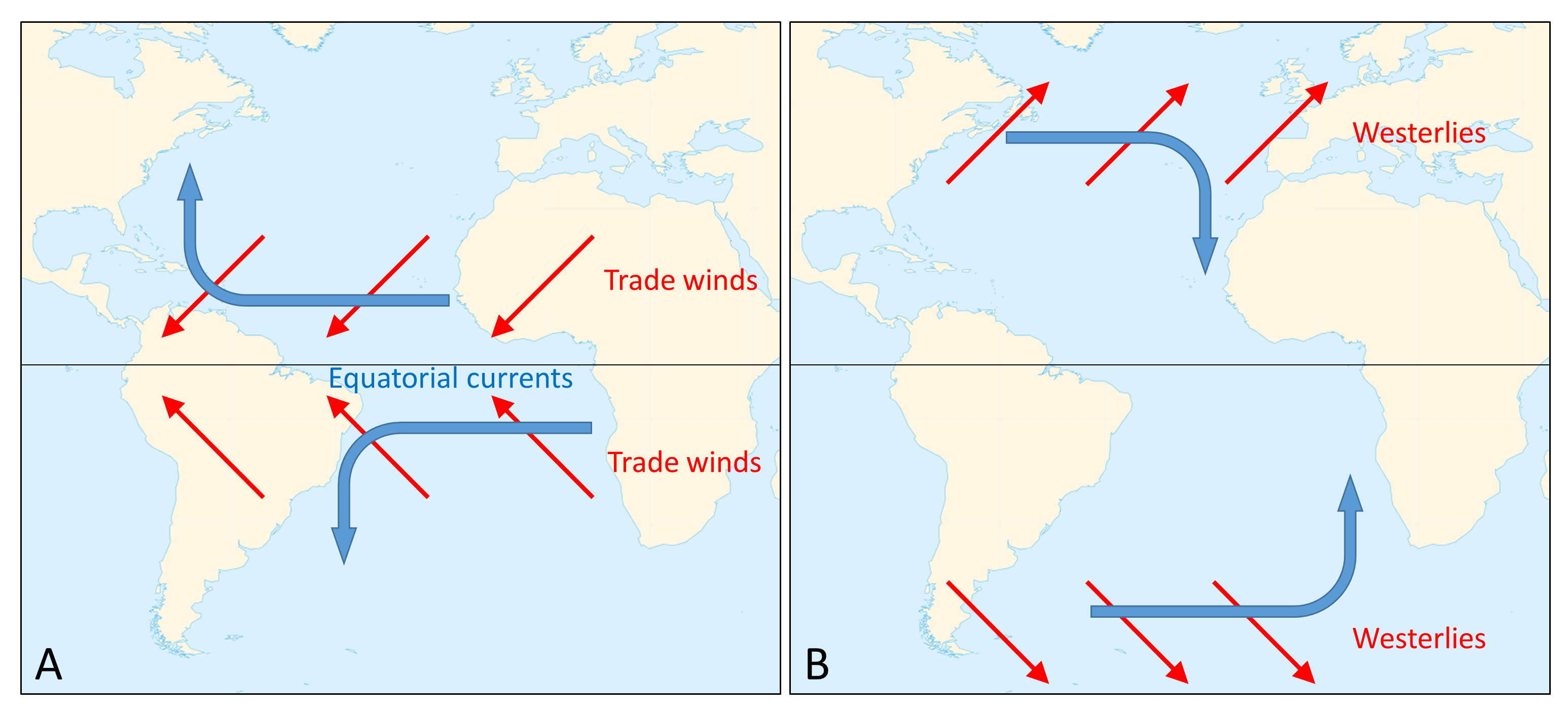
In one or two paragraphs, compare and contrast surface ... Surface currents refer to movement of the top layer of ocean water. Surface water flows in to replace the sinking water, which in turn becomes cold and salty enough to sink. examples of surface ocean currents are California Current (Cal) in the Pacific ocean basin and the Canary Current (Can) in the Atlantic ocean basin. Deep ocean currents PDF Activity: Ocean Currents There are: Surface currents are driven by wind and follow global atmospheric patterns. Cold surface currents move from the polar regions to the equatorial zones, and warm surface current move in the oppo site way. Deep currents are caused by the differences in water densities. Ocean Currents and Their Global Impact - Lesson The movements of currents are also constrained by the shape of the ocean basins. When a current runs into a continent, it must turn aside. The complex interplay between wind, gravity, Coriolis Effect, and topography determines the location, size, shape, and direction of the surface current gyres. (For example, consider this North Atlantic gyre. Ocean Currents and Climate - National Geographic Society worldwide movement of water (currents) in the ocean. ocean conveyor belt. Noun. system in which water moves between the cold depths and warm surface in oceans throughout the world. Also called thermohaline circulation. rip current. Noun. a strong flow of water running from the shore to the open ocean, sea, or lake.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › EarthEarth - Wikipedia This gives an apparent movement of the Sun eastward with respect to the stars at a rate of about 1°/day, which is one apparent Sun or Moon diameter every 12 hours. Due to this motion, on average it takes 24 hours—a solar day—for Earth to complete a full rotation about its axis so that the Sun returns to the meridian. The orbital speed of ... PDF CHAPTER SECTION 1 Currents - WPMU DEV Not all ocean currents are found at the surface. Movements of ocean water far below the surface are called deep currents. Unlike surface currents, deep currents are not controlled by wind. Deep current move-ments are controlled by water density. Density is the amount of matter in a given space or volume. The density of ocean water is affected by Thermohaline Circulation - Currents: NOAA's National Ocean ... Winds drive ocean currents in the upper 100 meters of the ocean's surface. However, ocean currents also flow thousands of meters below the surface. These deep-ocean currents are driven by differences in the water's density, which is controlled by temperature ( thermo) and salinity ( haline ). This process is known as thermohaline circulation. what is the difference between surface currents and deep ... What Is The Difference Between Surface Currents And Deep Currents?Surface currents are driven by global wind systems that are fueled by energy from the sun. ... Deep currents, also known as thermohaline circulation, result from differences in water density. These currents occur when cold, dense wat
PDF CHAPTER SECTION 1 Currents Movements of ocean water far below the surface are calleddeep currents. Unlike surface currents, deep currents are not controlled by wind. Deep current move- ments are controlled by water density. Densityis the amount of matter in a given space or volume. The density of ocean water is affected by temperature and salinity.
Compare and Contrast Deep ocean currents, and surface ... Surface currents are caused by wind blowing across the atlantic. (Affrects the top 30 feet) Surface currents Deep ocean currents Circulate tempature Move in a circular fomation called a Gyre. Colder water sinks and the warmer water rises to the top which helps bring oxygen down to animals at the bottom of the ocean. Show full text
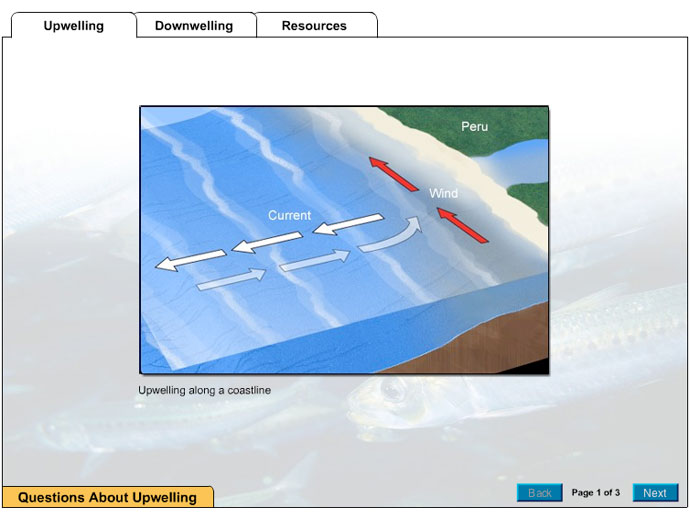
earthobservatory.nasa.gov › features › ElNinoEl Niño: Pacific Wind and Current Changes Bring Warm ... - NASA Feb 14, 2017 · For centuries, Peruvian fishermen reaped a bounty off the Pacific coast of South America, where north- and west-flowing currents pulled cool, nutrient-rich water from the deep. But every so often, the currents would stop or turn around; warm water from the tropics would drive the fish away and leave the nets empty.
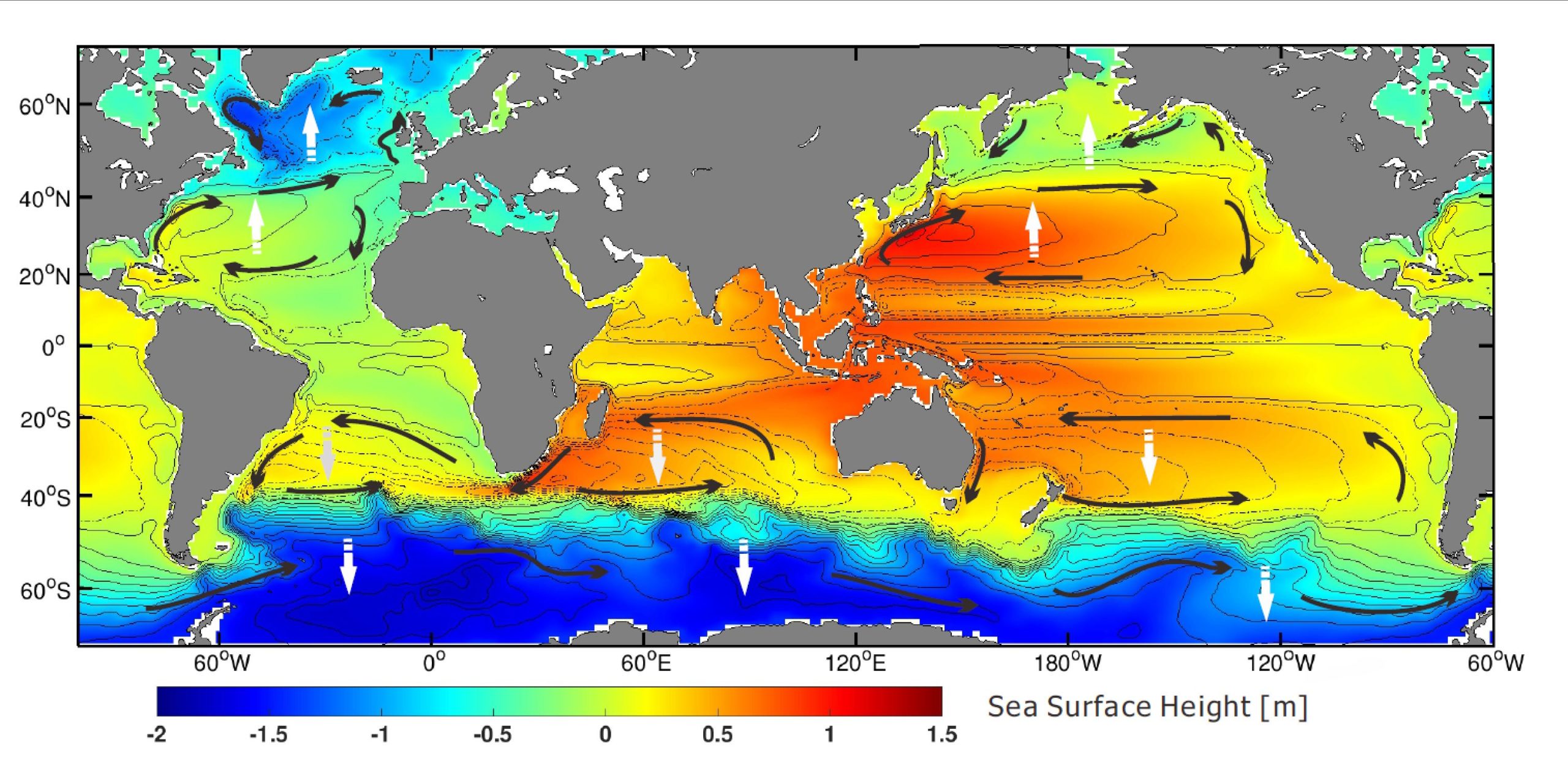
Ocean Circulation: Surface Water and Deep Water | Earth ... The colors are a bit hard for me to see, but note that in the North Atlantic, a surface current flows north and a deep current flows south. This means that deep water forms in the North Atlantic. It's important to appreciate that any Figure drawn at this scale, the entire ocean, is approximate.
Ocean Currents Flashcards - Quizlet Process that brings the deep cold ocean currents up to the surface. Convection currents. reason surface currents are at the surface of the ocean. they are warmer and less salty. Surface currents. A horizontal movement of ocean water that is caused by the wind which occurs at or near the oceans surface. Two types of ocean currents. Surface and ...
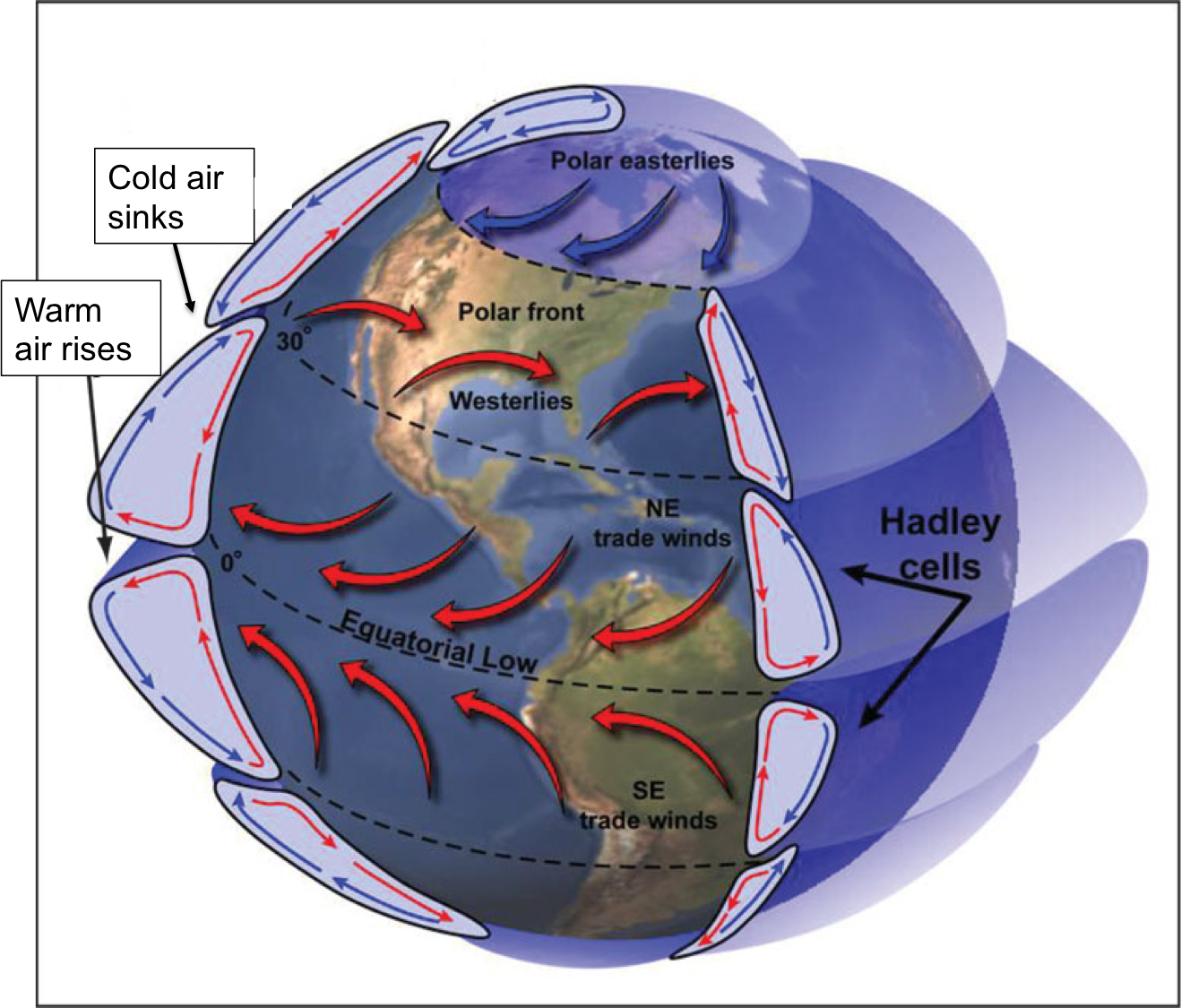
Ocean currents- The movement of life ⋆ TheScientificRevelation surface currents only comprise 10% of ocean circulation. The rest 90% comes under deep ocean circulation. Surface currents are driven mainly by wind and wind is driven by Coriolis force. This cycle starts with temperature. In the equatorial region which receives the highest amount of sunlight and heat, air starts to get heated and rise.
Ocean Surface Currents | manoa.hawaii.edu ... Surface currents are only 50 to 100 meters deep (Table 3.1). Though shallow, they are extremely important in determining the world's weather and climates, and in distributing the ocean's heat and nutrients. Winds are described by the direction from which they blow, whereas water currents are described by the direction toward which they flow.
What is the difference between surface current and deep ... Best Answer. Copy. Surface currents depend on temperature and wind which is in the atmosphere but deep water currents do not as it occurs under water. Wiki User. ∙ 2010-03-15 15:52:28. This ...
Horizontal and Vertical Ocean Currents - 1324 Words | 123 ... Ocean currents are horizontal or vertical movement of both surface and deep water throughout the world's oceans (Briney, n.d.). The primary generating forces are wind and differences in water density caused by variations in temperature and salinity. Currents generated by these forces are modified by factors such as the depth of the water ...
Upwelling and Downwelling in the ocean - Redmap Upwelling and downwelling describe mass movements of the ocean, which affect both surface and deep currents. These movements are essential in stirring the ocean, delivering oxygen to depth, distributing heat, and bringing nutrients to the surface. Upwelling is the movement of cold, deep, often nutrient-rich water to the surface mixed layer; and ...
manoa.hawaii.edu › exploringourfluidearthPhylum Mollusca | manoa.hawaii.edu/ExploringOurFluidEarth Introduction to Phylum Mollusca. The phylum Mollusca is the second-largest animal phylum, with over 100,000 species. The molluscs include many familiar animals, including clams, snails, slugs, and squid, as well as some less familiar animals, like tusk shells and chitons (Fig. 3.51 A).
Currents, Waves, and Tides | Smithsonian Ocean Currents. A large movement of water in one general direction is a current. Currents can be temporary or long-lasting. They can be near the surface or in the deep ocean. The strongest currents shape Earth's global climate patterns (and even local weather conditions) by moving heat around the world. Surface Currents
Ocean currents | National Oceanic and Atmospheric ... Ocean water is on the move, affecting your climate, your local ecosystem, and the seafood that you eat. Ocean currents, abiotic features of the environment, are continuous and directed movements of ocean water. These currents are on the ocean's surface and in its depths, flowing both locally and globally.
Understanding Surface Currents vs Deep Ocean Currents Deep currents are driven by temperature and water density/salinity. Of course, deep currents impact surface currents, which carry warm water to the poles. Surface currents are also driven by global wind systems fueled by energy from the sun. Factors like wind direction and the Coriolis effect play a role.
PDF Ocean Currents and Sea Surface Temperature Part I: Obtain maps of sea surface temperature (SST) and ocean surface winds from the Live Access Server. 1. Click on the link for the Live Access Server. 2. Click on 'Choose Dataset' if it does not automatically appear. Select Oceans, Daily Sea Surface Temperature (GHRSST). 3. For region, have students select their own from the drop-down menu.
Surface currents vs. Deep currents by Cedric Wright Surface currents vs. Deep currents Occur in water Are caused in three ways Used in oceans currents moving water can (on occasions) can go deep into water Deep Currents Surface Currents Both Movements deep inside water Carries cold water becomes warm movements on the surface of
Earth's Waters 4-4 Notes Flashcards - Quizlet Compare and contrast surface currents and deep currents. They are both are moving water that flows through oceans. Surface currents are towards the top of the ocean, can be warm or cold, and are controlled by winds. Deep currents are low, deep in the ocean, cold, and are controlled by density. How does upwelling effect marine life?






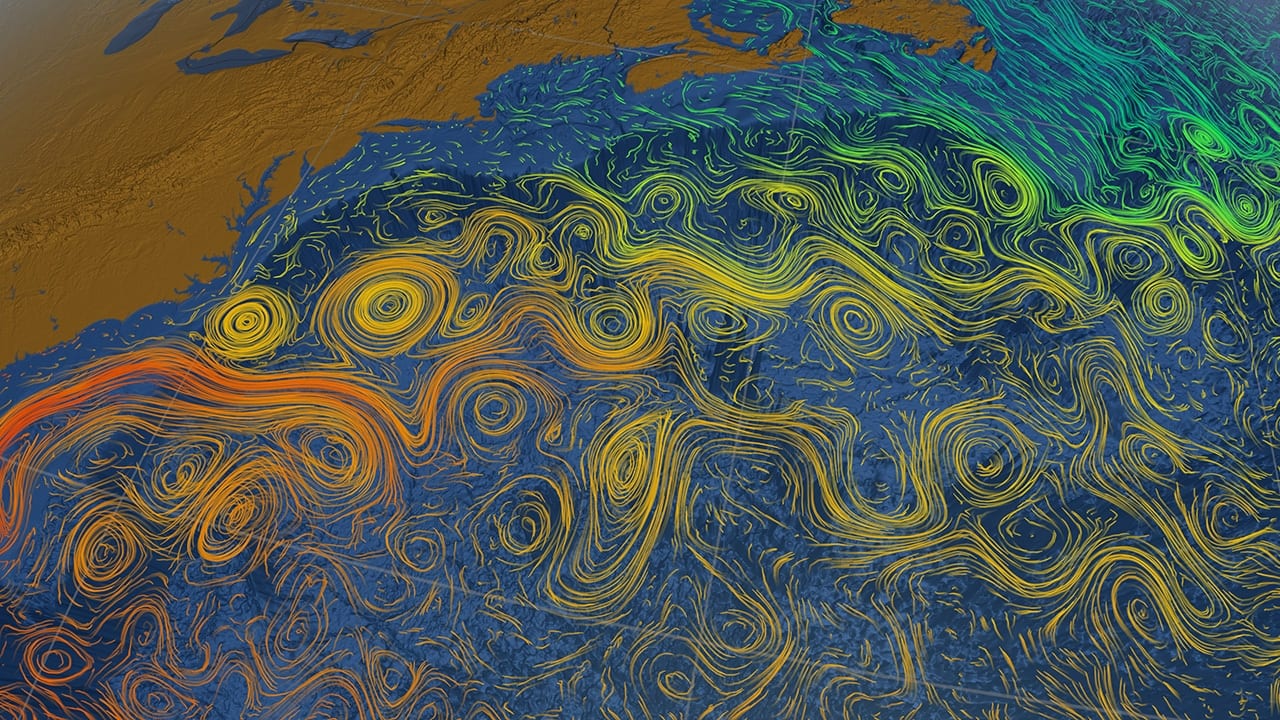
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/69/64/6964ec42-f74e-41eb-a7bd-4d2939689bd1/atlantic_currents.jpg)
















0 Response to "40 compare the movement of surface and deep currents"
Post a Comment